
application.properties 나 application.yml을 통해 property들을 설정할 때, 각 profile별로 값을 제대로 설정했는지 알고 싶을 때가 있다. 가령 “alpha” 프로파일에는 잘 되던 것이 다른 프로파일일 때는 잘 안되서 확인해봤더니 필요한 property를 빼먹고 설정하지 않을 때가 있다.
spring:
profiles: alpha
property:
option_0: option_0_value
option_1: option_1_value
...
---
spring:
profiles: beta
property:
option_0: option_0_value
위와 같이 option_1 property를 추가하고 배포할 때, beta 프로파일에서 해당 property를 추가하지 않아서 문제를 일으킬 것이다.
배포 중에 문제를 확인하여 고치지 말고 Spring Boot에서 지원하는 validation check 를 통해 테스트 중에 property들이 제대로 설정했는지 테스트를 할 수 있으면 좋을 것이다.
Spring Boot Reference Guide의 24.7.4 @ConfigurationProperties Validation 확인해보면 알겠지만 Spring Boot와 Hibernate, javax.validation 에서 제공하는 annotation을 통해 property를 설정했는지 안했는지 체크할 수 있다.
다음과 같이 application.yml 에 property들을 설정했다고 해보자.
mybatis:
config-location: classpath:db/mybatis-config.xml
mapper-locations: classpath:db/mapper/*.xml
type-aliases-package: com.example.dao
위의 property의 validation을 체크하기 위해 Spring Boot Reference Guide, 24.7 Type-safe Configuration Properties 절에 나와 있는 것 처럼 다음과 같이 클래스를 정의해야 한다.
import org.springframework.boot.context.properties.ConfigurationProperties;
import lombok.Data;
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "mybatis")
@Data
public class MybatisProperties {
private String configLocation;
private String mapperLocations;
private String typeAliasesPackage;
}
그리고 다음과 같이 Hibernate의 @NotEmpty annotation, 그리고 Spring Boot의 @Configuration, @Validated annotation을 통해 validation을 체크할 수 있다.
import org.hibernate.validator.constraints.NotEmpty;
import org.springframework.boot.context.properties.ConfigurationProperties;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.validation.annotation.Validated;
import lombok.Data;
@Configuration
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "mybatis")
@Validated
@Data
public class MybatisProperties {
@NotEmpty
private String configLocation;
@NotEmpty
private String mapperLocations;
@NotEmpty
private String typeAliasesPackage;
}
import org.junit.Test;
import org.junit.runner.RunWith;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;
import org.springframework.test.context.ActiveProfiles;
import org.springframework.test.context.junit4.SpringRunner;
import com.toast.cloud.image.properties.MybatisProperties;
@RunWith(SpringRunner.class)
@SpringBootTest
@ActiveProfiles("alpha")
public class AlphaPropertyValidationTest {
@Autowired
private MybatisProperties mybatisProperties;
@Test
public void test() {
...
}
}
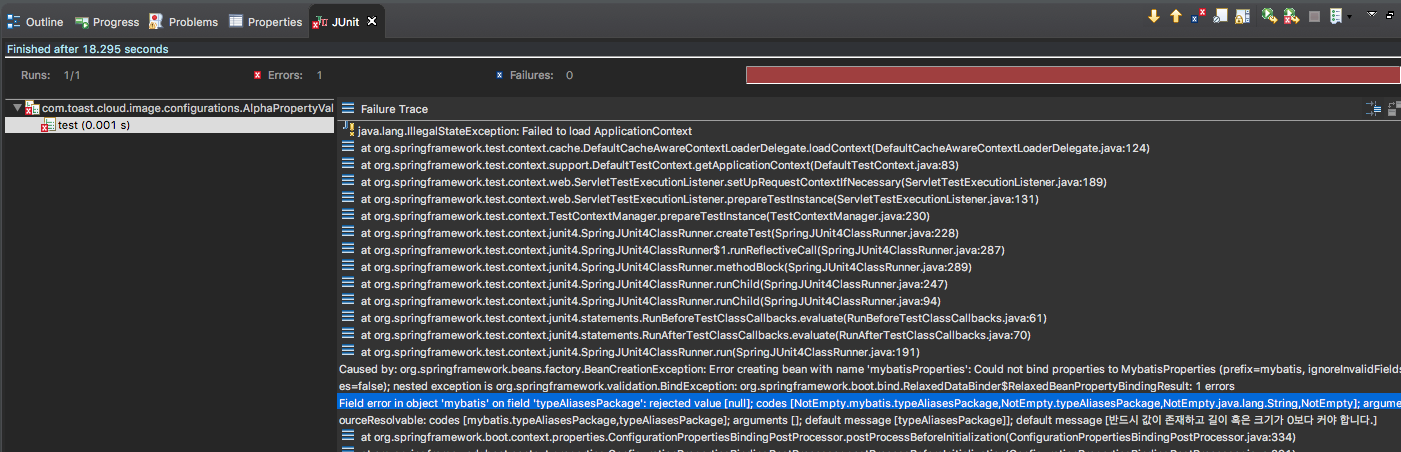
위와 같이 테스트 클래스에서 해당 property 클래스 오브젝트를 주입받고 테스트를 진행할 때, 만약 실수로 property 설정하는 것을 잊었다면 테스트 단계에서 걸러낼 수 있을 것이다. 만약 type-aliases-package property를 실수로 설정하지 않았다면 다음과 같이 테스트 과정에서 fail이 발생하는 것을 알 수 있다.
좀 더 복잡한 예를 살펴보자. 다음과 같이 property가 중첩되어 정의되어 있으면 어떻게 클래스를 정의할까?
spring:
datasource:
driver-class-name: com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
url: jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/sample_db?useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=UTF-8
username: sample
password: sample1234
위의 예에서는 spring - datasource - … 단계로 property가 중첩되어 있다. 이렇게 property가 중첩되어 정의되어 있으면 똑같이 클래스를 정의할 때도 static 이너 클래스를 추가로 정의하고 해당 클래스의 오브젝트를 필드로 정의해야 한다.
import javax.validation.Valid;
import org.hibernate.validator.constraints.NotEmpty;
import org.springframework.boot.context.properties.ConfigurationProperties;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.validation.annotation.Validated;
import lombok.Data;
@Configuration
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "spring")
@Validated
@Data
public class SpringProperties {
@Valid
private final DataSource datasource = new DataSource();
@Data
public static class DataSource {
@NotEmpty
private String driverClassName;
@NotEmpty
private String url;
@NotEmpty
private String username;
@NotEmpty
private String password;
}
}
위의 예에서 datasource 가 중첩되어 있는데 해당 부분을 static 이너 클래스로 정의하고, 안에 필드로써 property들을 정의하였다. 그리고 해당 클래스의 오브젝트를 필드로 정의하고, javax.validation의 @Valid annotation을 추가해주면 된다.