
Spring Boot 설명 / Spring Boot Refrence Guide Part 1/2 Review
Spring Boot는 Spring Framework를 사용하는 프로젝트를 아주 간편하게 셋업할 수 있는, Spring Framework의 서브 프로젝트이다. Spring application을 개발하는데 있어 필요한 의존성과 xml 구성 등의 일반적인 공통된 설정 작업을 자동으로 진행해주고, 개발자는 즉시 application 로직 개발을 시작할 수 있도록 지원하는 도구이다.
기존의 Spring framework를 이용한 개발환경 구축은 제법 많은 XML 설정파일들의 작성량을 요구했다. 그래서 잘 만들어놓은 설정 파일을 복사해서 사용하거나 검색을 통해 얻은 정보를 그대로 복사해서 사용하는 경우가 다반사였는데, 실상 특별한 경우의 설정을 제외하고는 거의 항상 동일한 옵션을 가져가게 되는 것이 사실이다.
Spring Boot는 Spring을 기반으로 하는, 바로 출시할 수 있는 수준의 ‘실행가능한’, 단독실행형 서버 애플리케이션을 만들기 위해 사용한다. Spring Platform과 서드파티 라이브러리들에 대한 선택을 최소한의 논의로 결정할 수 있도록 해준다. 그러한 부분에서 Spring Boot는 반복되는 개발환경 구축을 위한 코드 작성 등의 작업을 확연히 줄여주고, 빠르고 쉽게 프로젝트를 작성할 수 있도록 도와주는 것이다.
https://projects.spring.io/spring-boot/
Spring Boot를 이용해 -jar를 이용하여 Java 애플리케이션을 만들거나, 이전 외부 tomcat를 사용하는 것처럼 웹앱을 만들 수 있다.
하지만 gradle이나 maven과 같은 dependency management tool을 사용하는 것이 좋다. Spring Boot는 maven 3.2 / gradle 4 이상과 호환된다.
Spring Boot에 내장된 Servlet Container는 Spring Boot 2.0.3 기준으로 다음과 같이 지원한다.
| Name | Servlet Version | Java Version |
|---|---|---|
| Tomcat 8.5 | 3.1 | Java 7+ |
| Jetty 9.4 | 3.1 | Java 8+ |
| Undertow 1.4 | 3.1 | Java 7+ |
또한 Spring Boot 애플리케이션을 서블릿 3.1 이상을 지원하는 컨테이너에 배포 가능하다.
// ServletInitializer
package com.nhnent.hellospringboot;
import org.springframework.boot.builder.SpringApplicationBuilder;
import org.springframework.boot.web.support.SpringBootServletInitializer;
public class ServletInitializer extends SpringBootServletInitializer {
@Override
protected SpringApplicationBuilder configure(SpringApplicationBuilder application) {
return application.sources(HelloSpringBootApplication.class);
}
}
//HelloSpringBootApplication
package com.nhnent.hellospringboot;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
@SpringBootApplication
public class HelloSpringBootApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(HelloSpringBootApplication.class, args);
}
}
이 annotation은 Spring Boot의 가장 핵심적인 부분으로, 프로젝트 개발환경에서 많이 사용하는 annotation들을 쉽고 빠르게 사용할 수 있도록 다음과 같은 annotation들의 속성들을 포함하고 있는 annotation이다.
@EnableAutoConfiguration Spring Boot autoconfiguration은 추가된 jar dependency 기반으로 Spring application을 자동으로 설정하는 것을 시도한다. 예를 들어 HSQL DB가 class path에 있으면, DB 연결 빈을 정의하지 않아도 자동적으로 in-memory 데이터베이스에 접근할 것이다. 자동 설정은 비 침입적으로, DataSource 빈을 추가한다면 디폴트로 자동 설정되는 것은 사라질 것이다.
이 @SpringBootApplication annotation을 추적해보면, 이 클래스가 자바 Configuration을 사용하며, AutoConfiguration을 허용하며, 해당 Class가 있는 위치부터 컴포넌트를 스캔해서 빈으로 등록하는 것을 알 수 있다.
@Target(ElementType.TYPE)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
@Inherited
@SpringBootConfiguration
@EnableAutoConfiguration
@ComponentScan(excludeFilters = {
@Filter(type = FilterType.CUSTOM, classes = TypeExcludeFilter.class),
@Filter(type = FilterType.CUSTOM, classes = AutoConfigurationExcludeFilter.class) })
public @interface SpringBootApplication {
따라서 이 annotation이 선언된 메인 Spring Boot 애플리케이션 클래스는 프로젝트 패키지 루트에 지정하는 것이 좋다. 그래야 별다른 설정없이도 컴포넌트 스캔이 동작되어 클래스를 검색해 빈으로 등록할 수 있는 것이다.
이 annotation을 사용하게 되면 특별한 이유가 없는 한, 개발자는 자동설정을 별도로 할 필요가 없다.
Spring Boot의 자동 설정은 Java Configuration을 기반으로 하는데, 이와 관련된 설정은 이미 spring-boot-autoconfiguration 이라고 하는 프로젝트 안에 추가되어 있다.
여기서 우리가 사용하는 Web 과 관련된 WebMvcAutoConfiguration 을 살펴보자.
@Configuration
@ConditionalOnWebApplication
@ConditionalOnClass({ Servlet.class, DispatcherServlet.class, WebMvcConfigurerAdapter.class })
@ConditionalOnMissingBean(WebMvcConfigurationSupport.class)
@AutoConfigureOrder(Ordered.HIGHEST_PRECEDENCE + 10)
@AutoConfigureAfter(DispatcherServletAutoConfiguration.class)
public class WebMvcAutoConfiguration {
public static String DEFAULT_PREFIX = "";
public static String DEFAULT_SUFFIX = "";
@Bean
@ConditionalOnMissingBean(HiddenHttpMethodFilter.class)
public OrderedHiddenHttpMethodFilter hiddenHttpMethodFilter() {
return new OrderedHiddenHttpMethodFilter();
}
Servlet 및 DispatcherServlet, WebMvcConfigurerAdapter 클래스가 있고, WebMvcConfigurationSupport가 없을 때 우선권을 추가로 설정해서 빈을 등록하고, 이 설정 후에 DispatcherServletAutoConfiguration을 설정하라고 되어 있다.
//SpringApplication.run method
public static ConfigurableApplicationContext run(Object[] sources, String[] args) {
return new SpringApplication(sources).run(args);
}
이 메소드에서 하는 역할은 크게 두가지이다.
@SuppressWarnings({ "unchecked", "rawtypes" })
private void initialize(Object[] sources) {
if (sources != null && sources.length > 0) {
this.sources.addAll(Arrays.asList(sources));
}
this.webEnvironment = deduceWebEnvironment();
setInitializers((Collection) getSpringFactoriesInstances(
ApplicationContextInitializer.class));
setListeners((Collection) getSpringFactoriesInstances(ApplicationListener.class));
this.mainApplicationClass = deduceMainApplicationClass();
}
파라미터로 넘어간 application class를 바로 mainApplicationClass로 설정해도 될 것 같았지만, 그렇지 않고 deduceMainApplicationClass 함수를 사용하여 설정한다. 다음 코드와 같이 StackTrace를 사용해여 main 메소드를 가지는 클래스를 찾아 셋팅한다.
private Class<?> deduceMainApplicationClass() {
try {
StackTraceElement[] stackTrace = new RuntimeException().getStackTrace();
for (StackTraceElement stackTraceElement : stackTrace) {
if ("main".equals(stackTraceElement.getMethodName())) {ㄴ
return Class.forName(stackTraceElement.getClassName());
}
}
}
catch (ClassNotFoundException ex) {
// Swallow and continue
}
return null;
public ConfigurableApplicationContext run(String... args) {
StopWatch stopWatch = new StopWatch();
stopWatch.start();
ConfigurableApplicationContext context = null;
FailureAnalyzers analyzers = null;
configureHeadlessProperty();
SpringApplicationRunListeners listeners = getRunListeners(args);
listeners.starting();
try {
ApplicationArguments applicationArguments = new DefaultApplicationArguments(
args);
ConfigurableEnvironment environment = prepareEnvironment(listeners,
applicationArguments);
Banner printedBanner = printBanner(environment);
context = createApplicationContext();
analyzers = new FailureAnalyzers(context);
prepareContext(context, environment, listeners, applicationArguments,
printedBanner);
refreshContext(context);
afterRefresh(context, applicationArguments);
listeners.finished(context, null);
stopWatch.stop();
if (this.logStartupInfo) {
new StartupInfoLogger(this.mainApplicationClass)
.logStarted(getApplicationLog(), stopWatch);
}
return context;
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
handleRunFailure(context, listeners, analyzers, ex);
throw new IllegalStateException(ex);
}
}
package com.nhnent.hellospringboot.controller;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
@RestController
public class HelloRestController {
@RequestMapping("/")
public String index() {
return "Hello World!";
}
}
@RestController Spring 4.0에 추가된 annotation으로 @Controller 및 @ResponseBody 를 합쳐놓은 기능을 제공한다. @Conroller annotation과는 달리 요청을 처리하는 모든 메소드에 @ResponseBody를 추가할 필요가 없다. 또한 클래스에 속한 메소드들이 객체를 리턴할 때 JSON 형태로 직렬화된다. (Jackson2 라이브러리가 있다면.)
@ResponseBody 메소드에 이 annotation이 선언되어 있다면 메소드에서 리턴되는 값은 View를 통해 출력되지 않고, HTTP Response Body 에 직접 쓰여지게 된다.
Spring Boot는 별다른 설정없이 즉시 시작할 수 있는 프로퍼티 환경을 제공한다. 디렉토리 내 ‘resources’ 하위에 ‘application.properties’ 라는 파일을 생성해두면 기본적으로 해당 파일에 있는 프로퍼티를 Spring Boot가 참조한다.
사용되는 property는 이 포스트의 하단에 첨부하였으니 참고
application.properties 파일을 다음과 같이 작성한다.
hello_spring_boot.print.hello=Hello Spring Boot!
그리고 다음과 같이 /로 접속했을 때 출력할 수 있도록 @Value annotation을 사용해서 실험해본다.
@RestController
public class HelloRestController {
@Value("${hello_spring_boot.print.hello}")
private String hello_string;
@RequestMapping("/")
public String index() {
return hello_string;
}
}
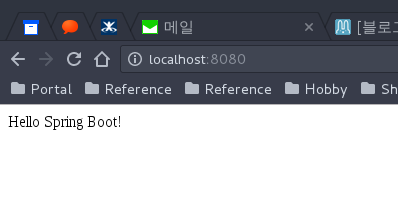
그러면 localhost로 접속했을 때 다음과 같이 application.properties에 추가한 것이 출력되는 것을 확인할 수 있다.
# ===================================================================
# COMMON SPRING BOOT PROPERTIES
#
# This sample file is provided as a guideline. Do NOT copy it in its
# entirety to your own application. ^^^
# ===================================================================
# ----------------------------------------
# CORE PROPERTIES
# ----------------------------------------
# BANNER
banner.charset=UTF-8 # Banner file encoding.
(배너 인코딩 설정)
banner.location=classpath:banner.txt # Banner file location.
(배너 파일 위치)
# LOGGING
logging.config= # Location of the logging configuration file. For instance `classpath:logback.xml` for Logback)
(로깅 파일 위치)
logging.exception-conversion-word=%wEx # Conversion word used when logging exceptions.
(로깅 exception 사용시 conversion word사용)
logging.file= # Log file name. For instance `myapp.log`
(로그 파일 이름)
logging.level.*= # Log levels severity mapping. For instance `logging.level.org.springframework=DEBUG`
(로그 찍을 레벨)
logging.path= # Location of the log file. For instance `/var/log`
(로깅 파일 위치)
logging.pattern.console= # Appender pattern for output to the console. Only supported with the default logback setup.
(콘솔 로깅에 붙일 패턴)
logging.pattern.file= # Appender pattern for output to the file. Only supported with the default logback setup.
(파일 로깅에 붙일 패턴)
logging.pattern.level= # Appender pattern for log level (default %5p). Only supported with the default logback setup.
(로그레벨에 붙일 패턴)
logging.register-shutdown-hook=false # Register a shutdown hook for the logging system when it is initialized.
(로깅시스템 shutdown hook 설정)
# AOP
spring.aop.auto=true # Add @EnableAspectJAutoProxy.
(AOP 자동 사용 설정)
spring.aop.proxy-target-class=false # Whether subclass-based (CGLIB) proxies are to be created (true) as opposed to standard Java interface-based proxies (false).
(subclass-based aop 사용 여부)
# IDENTITY (ContextIdApplicationContextInitializer)
spring.application.index= # Application index.
(애플리케이션 인덱스)
spring.application.name= # Application name.
(애플리케이션 이름)
# ADMIN (SpringApplicationAdminJmxAutoConfiguration)
spring.application.admin.enabled=false # Enable admin features for the application.
(애플리케이션 관리자 활성화)
spring.application.admin.jmx-name=org.springframework.boot:type=Admin,name=SpringApplication # JMX name of the application admin MBean.
(애플리케이션 관리자 jmx이름 설정)
(JMX는 java management extension의 약자이다.
JDK 1.5부터 기본적으로 탑재되어 제공되고 있다.
Application 관리를 위한 다양한 기능을 제공할 목적으로 시작되었다.
Non-Java resources와 하드웨어에 대해 wrapping한 인터페이스를 제공하며,
API를 외부로 노출해 application 설정 및 통계데이터를 수집할수도 있다.)
# AUTO-CONFIGURATION
spring.autoconfigure.exclude= # Auto-configuration classes to exclude.
(spring의 autoconfiguration 제외 여부)
# SPRING CORE
spring.beaninfo.ignore=true # Skip search of BeanInfo classes.
(BeanInfo class 검색 무시)
# SPRING CACHE (CacheProperties)
spring.cache.cache-names= # Comma-separated list of cache names to create if supported by the underlying cache manager.
(스프링 캐쉬 이름 설정)
spring.cache.ehcache.config= # The location of the configuration file to use to initialize EhCache.
(스프링 캐쉬 설정 파일 위치)
spring.cache.guava.spec= # The spec to use to create caches. Check CacheBuilderSpec for more details on the spec format.
(캐쉬 guava 스펙)
spring.cache.hazelcast.config= # The location of the configuration file to use to initialize Hazelcast.
(캐쉬 hazelcast 설정 위치)
spring.cache.infinispan.config= # The location of the configuration file to use to initialize Infinispan.
(캐쉬 infinispan 설정 위치)
spring.cache.jcache.config= # The location of the configuration file to use to initialize the cache manager.
(jcash 설정 위치)
spring.cache.jcache.provider= # Fully qualified name of the CachingProvider implementation to use to retrieve the JSR-107 compliant cache manager. Only needed if more than one JSR-107 implementation is available on the classpath.
(캐쉬추가 이름)
spring.cache.type= # Cache type, auto-detected according to the environment by default.
(캐쉬 타입)
# SPRING CONFIG - using environment property only (ConfigFileApplicationListener)
spring.config.location= # Config file locations.
(스프링 설정 파일 위치)
spring.config.name=application # Config file name.
(스프링 설정 파일 이름)
# HAZELCAST (HazelcastProperties)
spring.hazelcast.config= # The location of the configuration file to use to initialize Hazelcast.
(스프링 hazelcast 설정 파일 위치)
(hazelcast : 프로그램들을 그룹화(clustering)해서 그룹 간에 데이터를 가변적으로 분산시켜주기 위한 것)
# JMX
spring.jmx.default-domain= # JMX domain name.
(jmx 기본 도메인 이름)
spring.jmx.enabled=true # Expose management beans to the JMX domain.
(jmx 도메인 사용 여부)
spring.jmx.server=mbeanServer # MBeanServer bean name.
(jmx server 이름)
# Email (MailProperties)
spring.mail.default-encoding=UTF-8 # Default MimeMessage encoding.
(이메일 인코딩)
spring.mail.host= # SMTP server host. For instance `smtp.example.com`
(이메일 호스트 주소)
spring.mail.jndi-name= # Session JNDI name. When set, takes precedence to others mail settings.
(세션 JNDI 이름)
spring.mail.password= # Login password of the SMTP server.
(SMTP서버 패스워드)
spring.mail.port= # SMTP server port.
(SMTP서버 포트)
spring.mail.properties.*= # Additional JavaMail session properties.
(추가적인 javamail 세션 속성)
spring.mail.protocol=smtp # Protocol used by the SMTP server.
(SMTP서버 프로토콜)
spring.mail.test-connection=false # Test that the mail server is available on startup.
(시작시 mail server 테스트 여부)
spring.mail.username= # Login user of the SMTP server.
(mail server 로그인 유저 이름)
# APPLICATION SETTINGS (SpringApplication)
spring.main.banner-mode=console # Mode used to display the banner when the application runs.
(배너 모드 설정 - 어디에 display할건지)
spring.main.sources= # Sources (class name, package name or XML resource location) to include in the ApplicationContext.
(배너 위치)
spring.main.web-environment= # Run the application in a web environment (auto-detected by default).
(application을 web environment에서 시작 할 것인지 여부)
# FILE ENCODING (FileEncodingApplicationListener)
spring.mandatory-file-encoding= # Expected character encoding the application must use.
(file 인코딩 종류)
# INTERNATIONALIZATION (MessageSourceAutoConfiguration)
spring.messages.basename=messages # Comma-separated list of basenames, each following the ResourceBundle convention.
(스프링 메시지)
spring.messages.cache-seconds=-1 # Loaded resource bundle files cache expiration, in seconds. When set to -1, bundles are cached forever.
(스프링 캐쉬 관련)
spring.messages.encoding=UTF-8 # Message bundles encoding.
(메시지 인코딩)
spring.messages.fallback-to-system-locale=true # Set whether to fall back to the system Locale if no files for a specific Locale have been found.
(fallback 여부)
# OUTPUT
spring.output.ansi.enabled=detect # Configure the ANSI output (can be "detect", "always", "never").
(결과물 속성)
# PID FILE (ApplicationPidFileWriter)
spring.pid.fail-on-write-error= # Fail if ApplicationPidFileWriter is used but it cannot write the PID file.
(pid 파일 에러 여부)
spring.pid.file= # Location of the PID file to write (if ApplicationPidFileWriter is used).
(pid 파일 위치)
# PROFILES
spring.profiles.active= # Comma-separated list of active profiles.
(스프링 프로파일 active)
spring.profiles.include= # Unconditionally activate the specified comma separated profiles.
(스프링 프로파일 추가)
# SENDGRID (SendGridAutoConfiguration)
spring.sendgrid.username= # SendGrid account username
(스프링 sendgrid 이름)
(SendGrid is a cloud-based SMTP provider that allows you to send email without having to maintain email servers.)
spring.sendgrid.password= # SendGrid account password
(snedgrid 패스워드)
spring.sendgrid.proxy.host= # SendGrid proxy host
(sendgrid 호스트 서버)
spring.sendgrid.proxy.port= # SendGrid proxy port
(sendgrid 호스트 포트)
# ----------------------------------------
# WEB PROPERTIES
# ----------------------------------------
# MULTIPART (MultipartProperties)
multipart.enabled=true # Enable support of multi-part uploads.
(multipart upload 사용 여부) - 파일 업로드 데이터 형식
multipart.file-size-threshold=0 # Threshold after which files will be written to disk. Values can use the suffixed "MB" or "KB" to indicate a Megabyte or Kilobyte size.
(멀티파트 파일 사이즈 trheshold)
multipart.location= # Intermediate location of uploaded files.
(업로드된 파일의 파일 주소)
multipart.max-file-size=1Mb # Max file size. Values can use the suffixed "MB" or "KB" to indicate a Megabyte or Kilobyte size.
(최대 파일 사이즈)
multipart.max-request-size=10Mb # Max request size. Values can use the suffixed "MB" or "KB" to indicate a Megabyte or Kilobyte size.
(최대 요청 사이즈)
# EMBEDDED SERVER CONFIGURATION (ServerProperties)
server.address= # Network address to which the server should bind to.
(bind 될 서버 주소)
server.compression.enabled=false # If response compression is enabled.
(서버 compression 사용 여부)
server.compression.excluded-user-agents= # List of user-agents to exclude from compression.
(추가적인 useragents)
server.compression.mime-types= # Comma-separated list of MIME types that should be compressed. For instance `text/html,text/css,application/json`
(mime 타입설정)
server.compression.min-response-size= # Minimum response size that is required for compression to be performed. For instance 2048
(최소 response 사이즈)
server.context-parameters.*= # Servlet context init parameters. For instance `server.context-parameters.a=alpha`
(서버 파라미터)
server.context-path= # Context path of the application.
(서버 애플리케이션 context path)
server.display-name=application # Display name of the application.
(서버 애플리케이션 이름 보이기)
server.error.include-stacktrace=never # When to include a "stacktrace" attribute.
(서버에러시에 stacktrace할것인지 여부)
server.error.path=/error # Path of the error controller.
(서버 에러 위치)
server.error.whitelabel.enabled=true # Enable the default error page displayed in browsers in case of a server error.
(에러 whitelabel 사용 여부)
server.jsp-servlet.class-name=org.apache.jasper.servlet.JspServlet # The class name of the JSP servlet.
(jsp servlet 클래스이름)
server.jsp-servlet.init-parameters.*= # Init parameters used to configure the JSP servlet
(jsp servlet 초기화 파라미터 )
server.jsp-servlet.registered=true # Whether or not the JSP servlet is registered
(jsp servlet 등록)
server.port=8080 # Server HTTP port.
(서버 포트)
server.server-header= # The value sent in the server response header (uses servlet container default if empty)
(서버 헤더)
server.servlet-path=/ # Path of the main dispatcher servlet.
(서버 서플릿 path)
server.session.cookie.comment= # Comment for the session cookie.
(세션 쿠키 주석)
server.session.cookie.domain= # Domain for the session cookie.
(세션 쿠키 도메인 주소)
server.session.cookie.http-only= # "HttpOnly" flag for the session cookie.
(http only cookie 설정)
server.session.cookie.max-age= # Maximum age of the session cookie in seconds.
(세션 max-age seconds 속성)
server.session.cookie.name= # Session cookie name.
(세션 쿠키 이름)
server.session.cookie.path= # Path of the session cookie.
(세션 쿠키 path)
server.session.cookie.secure= # "Secure" flag for the session cookie.
(세션 쿠키 secure)
server.session.persistent=false # Persist session data between restarts.
(세션 쿠키 다시 시작 여부)
server.session.store-dir= # Directory used to store session data.
(세션 저장 위치)
server.session.timeout= # Session timeout in seconds.
(세션 timeout 시간 설정)
server.session.tracking-modes= # Session tracking modes (one or more of the following: "cookie", "url", "ssl").
(세션 tracking mode)
server.ssl.ciphers= # Supported SSL ciphers.
(ssl 관련 속성)
server.ssl.client-auth= # Whether client authentication is wanted ("want") or needed ("need"). Requires a trust store.
server.ssl.enabled= #
server.ssl.key-alias= #
server.ssl.key-password= #
server.ssl.key-store= #
server.ssl.key-store-password= #
server.ssl.key-store-provider= #
server.ssl.key-store-type= #
server.ssl.protocol= #
server.ssl.trust-store= #
server.ssl.trust-store-password= #
server.ssl.trust-store-provider= #
server.ssl.trust-store-type= #
server.tomcat.accesslog.directory=logs # Directory in which log files are created. Can be relative to the tomcat base dir or absolute.
(톰켓 accesslog 파일 위치)
server.tomcat.accesslog.enabled=false # Enable access log.
(톰켓 accesslog 여부)
server.tomcat.accesslog.pattern=common # Format pattern for access logs.
(톰캣 로그파일에 붙일 패턴)
server.tomcat.accesslog.prefix=access_log # Log file name prefix.
(톰캣 엑세스로그파일 앞에 붙일 이름)
server.tomcat.accesslog.suffix=.log # Log file name suffix.
(톰켓 엑세스로그파일 뒤에 붙일 이름)
server.tomcat.background-processor-delay=30 # Delay in seconds between the invocation of backgroundProcess methods.
(백그라운드 delay second 설정)
server.tomcat.basedir= # Tomcat base directory. If not specified a temporary directory will be used.
(톰켓 base directory 설정)
server.tomcat.internal-proxies=10\\.\\d{1,3}\\.\\d{1,3}\\.\\d{1,3}|\\
192\\.168\\.\\d{1,3}\\.\\d{1,3}|\\
169\\.254\\.\\d{1,3}\\.\\d{1,3}|\\
127\\.\\d{1,3}\\.\\d{1,3}\\.\\d{1,3}|\\
172\\.1[6-9]{1}\\.\\d{1,3}\\.\\d{1,3}|\\
172\\.2[0-9]{1}\\.\\d{1,3}\\.\\d{1,3}|\\
172\\.3[0-1]{1}\\.\\d{1,3}\\.\\d{1,3} # regular expression matching trusted IP addresses.
(톰켓 internap ip adress 속성 설정)
server.tomcat.max-http-header-size=0 # Maximum size in bytes of the HTTP message header.
(max http header 사이즈 설정)
server.tomcat.max-threads=0 # Maximum amount of worker threads.
(최대 스레드 설정)
server.tomcat.port-header=X-Forwarded-Port # Name of the HTTP header used to override the original port value.
(톰켓 포트 헤더)
server.tomcat.protocol-header= # Header that holds the incoming protocol, usually named "X-Forwarded-Proto".
(톰켓 프로토콜 헤더)
server.tomcat.protocol-header-https-value=https # Value of the protocol header that indicates that the incoming request uses SSL.
(헤더 http value 설정)
server.tomcat.remote-ip-header= # Name of the http header from which the remote ip is extracted. For instance `X-FORWARDED-FOR`
(ip header 설정)
server.tomcat.uri-encoding=UTF-8 # Character encoding to use to decode the URI.
(uri 인코딩 설정)
server.undertow.accesslog.dir= # Undertow access log directory.
(undertow의 accesslog 파일 위치)
(Undertow는 Java로 작성된 유연하면서 고성능의 웹서버이며 NIO기반의 blogcking / Non-blocking API를 제공한다.
Undertow는 컴퍼지션 아키텍처를 제공하여 작은 단위의 용도를 갖는 핸들러들를 연결하여 웹서버를 구축 할 수 있다.
컴포지션 아키텍처는 Full Java EE Servlet 3.1 컨테이너에서 부터 Low Level의 Non-blocking 핸들러
또는 그 중간 수준의 기능을 선택을 할 수 있는 유연성을 제공해 준다.)
server.undertow.accesslog.enabled=false # Enable access log.
server.undertow.accesslog.pattern=common # Format pattern for access logs.
server.undertow.buffer-size= # Size of each buffer in bytes.
server.undertow.buffers-per-region= # Number of buffer per region.
server.undertow.direct-buffers= # Allocate buffers outside the Java heap.
server.undertow.io-threads= # Number of I/O threads to create for the worker.
server.undertow.worker-threads= # Number of worker threads.
server.use-forward-headers= # If X-Forwarded-* headers should be applied to the HttpRequest.
(foward header 사용)
# FREEMARKER (FreeMarkerAutoConfiguration)
(FreeMarker는 Velocity와 마찬가지로 templating 언어이다.
우리가 Jsp를 코딩하다보면 날코딩으로 생산성이 떨어진다.
그래서 우리는 좀더 편리하게 사용하기위해서 템플릿 엔진을 사용한다.
그리고 가장 큰 장점은 매크로 기능으로 기능을 만들어서 사용할 수 있다는 점이다.)
spring.freemarker.allow-request-override=false # Set whether HttpServletRequest attributes are allowed to override (hide) controller generated model attributes of the same name.
spring.freemarker.allow-session-override=false # Set whether HttpSession attributes are allowed to override (hide) controller generated model attributes of the same name.
spring.freemarker.cache=false # Enable template caching.
spring.freemarker.charset=UTF-8 # Template encoding.
spring.freemarker.check-template-location=true # Check that the templates location exists.
spring.freemarker.content-type=text/html # Content-Type value.
spring.freemarker.enabled=true # Enable MVC view resolution for this technology.
spring.freemarker.expose-request-attributes=false # Set whether all request attributes should be added to the model prior to merging with the template.
spring.freemarker.expose-session-attributes=false # Set whether all HttpSession attributes should be added to the model prior to merging with the template.
spring.freemarker.expose-spring-macro-helpers=true # Set whether to expose a RequestContext for use by Spring's macro library, under the name "springMacroRequestContext".
spring.freemarker.prefer-file-system-access=true # Prefer file system access for template loading. File system access enables hot detection of template changes.
spring.freemarker.prefix= # Prefix that gets prepended to view names when building a URL.
spring.freemarker.request-context-attribute= # Name of the RequestContext attribute for all views.
spring.freemarker.settings.*= # Well-known FreeMarker keys which will be passed to FreeMarker's Configuration.
spring.freemarker.suffix= # Suffix that gets appended to view names when building a URL.
spring.freemarker.template-loader-path=classpath:/templates/ # Comma-separated list of template paths.
spring.freemarker.view-names= # White list of view names that can be resolved
# GROOVY TEMPLATES (GroovyTemplateAutoConfiguration)
(그루비 템플릿 - 타입아 유연하고 간결한 동적 객체지향 언어 관련 옵션)
spring.groovy.template.allow-request-override=false # Set whether HttpServletRequest attributes are allowed to override (hide) controller generated model attributes of the same name.
spring.groovy.template.allow-session-override=false # Set whether HttpSession attributes are allowed to override (hide) controller generated model attributes of the same name.
spring.groovy.template.cache= # Enable template caching.
spring.groovy.template.charset=UTF-8 # Template encoding.
spring.groovy.template.check-template-location=true # Check that the templates location exists.
spring.groovy.template.configuration.*= # See GroovyMarkupConfigurer
spring.groovy.template.content-type=test/html # Content-Type value.
spring.groovy.template.enabled=true # Enable MVC view resolution for this technology.
spring.groovy.template.expose-request-attributes=false # Set whether all request attributes should be added to the model prior to merging with the template.
spring.groovy.template.expose-session-attributes=false # Set whether all HttpSession attributes should be added to the model prior to merging with the template.
spring.groovy.template.expose-spring-macro-helpers=true # Set whether to expose a RequestContext for use by Spring's macro library, under the name "springMacroRequestContext".
spring.groovy.template.prefix= # Prefix that gets prepended to view names when building a URL.
spring.groovy.template.request-context-attribute= # Name of the RequestContext attribute for all views.
spring.groovy.template.resource-loader-path=classpath:/templates/ # Template path.
spring.groovy.template.suffix=.tpl # Suffix that gets appended to view names when building a URL.
spring.groovy.template.view-names= # White list of view names that can be resolved.
# SPRING HATEOAS (HateoasProperties)
spring.hateoas.use-hal-as-default-json-media-type=true # Specify if application/hal+json responses should be sent to requests that accept application/json.
(HATEOASHATEOAS는 RESTful API를 사용하는 클라이언트가 전적으로 서버에 의해 동적으로 상호작용을 할 수 있다. 쉽게 말하면 클라이언트가 서버에 요청시 서버는 요청에 의존되는 URI를 Response에 포함시켜 반환한다. 옵션)
(http://blog.woniper.net/219)
# HTTP message conversion
spring.http.converters.preferred-json-mapper=jackson # Preferred JSON mapper to use for HTTP message conversion. Set to "gson" to force the use of Gson when both it and Jackson are on the classpath.
(http message 설정)
# HTTP encoding (HttpEncodingProperties)
spring.http.encoding.charset=UTF-8 # Charset of HTTP requests and responses. Added to the "Content-Type" header if not set explicitly.
(http encoding 설정)
spring.http.encoding.enabled=true # Enable http encoding support.
(http 인코딩 여부)
spring.http.encoding.force=true # Force the encoding to the configured charset on HTTP requests and responses.
(http 인코딩 강제 여부)
# JACKSON (JacksonProperties)
(스프링 json 자동 생성 관련 속성)
spring.jackson.date-format= # Date format string or a fully-qualified date format class name. For instance `yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss`
spring.jackson.deserialization.*= # Jackson on/off features that affect the way Java objects are deserialized.
spring.jackson.generator.*= # Jackson on/off features for generators.
spring.jackson.joda-date-time-format= # Joda date time format string. If not configured, "date-format" will be used as a fallback if it is configured with a format string.
spring.jackson.locale= # Locale used for formatting.
spring.jackson.mapper.*= # Jackson general purpose on/off features.
spring.jackson.parser.*= # Jackson on/off features for parsers.
spring.jackson.property-naming-strategy= # One of the constants on Jackson's PropertyNamingStrategy. Can also be a fully-qualified class name of a PropertyNamingStrategy subclass.
spring.jackson.serialization.*= # Jackson on/off features that affect the way Java objects are serialized.
spring.jackson.serialization-inclusion= # Controls the inclusion of properties during serialization. Configured with one of the values in Jackson's JsonInclude.Include enumeration.
spring.jackson.time-zone= # Time zone used when formatting dates. For instance `America/Los_Angeles`
# JERSEY (JerseyProperties)
(스프링을 이용하여 RESTFul api를 만드는데 도와줌)
spring.jersey.application-path= # Path that serves as the base URI for the application. Overrides the value of "@ApplicationPath" if specified.
spring.jersey.filter.order=0 # Jersey filter chain order.
spring.jersey.init.*= # Init parameters to pass to Jersey via the servlet or filter.
spring.jersey.type=servlet # Jersey integration type. Can be either "servlet" or "filter".
# SPRING MOBILE DEVICE VIEWS (DeviceDelegatingViewResolverAutoConfiguration)
(스프링 모바일 디바이스 뷰 속성)
spring.mobile.devicedelegatingviewresolver.enable-fallback=false # Enable support for fallback resolution.
spring.mobile.devicedelegatingviewresolver.enabled=false # Enable device view resolver.
spring.mobile.devicedelegatingviewresolver.mobile-prefix=mobile/ # Prefix that gets prepended to view names for mobile devices.
spring.mobile.devicedelegatingviewresolver.mobile-suffix= # Suffix that gets appended to view names for mobile devices.
spring.mobile.devicedelegatingviewresolver.normal-prefix= # Prefix that gets prepended to view names for normal devices.
spring.mobile.devicedelegatingviewresolver.normal-suffix= # Suffix that gets appended to view names for normal devices.
spring.mobile.devicedelegatingviewresolver.tablet-prefix=tablet/ # Prefix that gets prepended to view names for tablet devices.
spring.mobile.devicedelegatingviewresolver.tablet-suffix= # Suffix that gets appended to view names for tablet devices.
# SPRING MOBILE SITE PREFERENCE (SitePreferenceAutoConfiguration)
spring.mobile.sitepreference.enabled=true # Enable SitePreferenceHandler.
(스프링 모바일 속성 사이트 여부)
# MUSTACHE TEMPLATES (MustacheAutoConfiguration)
(Mustache template 속성 선언)
(Mustache는 제어 구조를 갖춘 것 중 문법이 간단하고 가장 많은 언어로 포팅된 템플릿 엔진입니다.
Mustache를 기반으로 이를 확장한 템플릿 엔진도 여럿 있는데 대표적으로는 헬퍼 개념을 추가한
Handlebars와 트위터에서 만든 Hogan.js를 들 수 있다.)
spring.mustache.cache=false # Enable template caching.
spring.mustache.charset=UTF-8 # Template encoding.
spring.mustache.check-template-location=true # Check that the templates location exists.
spring.mustache.content-type=text/html # Content-Type value.
spring.mustache.enabled=true # Enable MVC view resolution for this technology.
spring.mustache.prefix=classpath:/templates/ # Prefix to apply to template names.
spring.mustache.suffix=.html # Suffix to apply to template names.
spring.mustache.view-names= # White list of view names that can be resolved.
# SPRING MVC (WebMvcProperties)
(스프링 mvc 관련 옵션들)
spring.mvc.async.request-timeout= # Amount of time (in milliseconds) before asynchronous request handling times out.
spring.mvc.date-format= # Date format to use. For instance `dd/MM/yyyy`.
spring.mvc.dispatch-trace-request=false # Dispatch TRACE requests to the FrameworkServlet doService method.
spring.mvc.dispatch-options-request=false # Dispatch OPTIONS requests to the FrameworkServlet doService method.
spring.mvc.favicon.enabled=true # Enable resolution of favicon.ico.
spring.mvc.ignore-default-model-on-redirect=true # If the content of the "default" model should be ignored during redirect scenarios.
spring.mvc.locale= # Locale to use.
spring.mvc.media-types.*= # Maps file extensions to media types for content negotiation.
spring.mvc.message-codes-resolver-format= # Formatting strategy for message codes. For instance `PREFIX_ERROR_CODE`.
spring.mvc.static-path-pattern=/** # Path pattern used for static resources.
spring.mvc.throw-exception-if-no-handler-found=false # If a "NoHandlerFoundException" should be thrown if no Handler was found to process a request.
spring.mvc.view.prefix= # Spring MVC view prefix.
spring.mvc.view.suffix= # Spring MVC view suffix.
# SPRING RESOURCES HANDLING (ResourceProperties)
(스프링 리소스 핸들링 관련 속성)
spring.resources.add-mappings=true # Enable default resource handling.
(스프링 리소스 핸들링 enable)
spring.resources.cache-period= # Cache period for the resources served by the resource handler, in seconds.
(스프링 리소스 캐쉬 관련 속성)
spring.resources.chain.cache=true # Enable caching in the Resource chain.
(리소스 체인 캐쉬 활성화)
spring.resources.chain.enabled= # Enable the Spring Resource Handling chain. Disabled by default unless at least one strategy has been enabled.
(리소스 체인 활성화)
spring.resources.chain.html-application-cache=false # Enable HTML5 application cache manifest rewriting.
(html5 캐쉬 속성 활성화)
spring.resources.chain.strategy.content.enabled=false # Enable the content Version Strategy.
(strategy content 활성화)
spring.resources.chain.strategy.content.paths=/** # Comma-separated list of patterns to apply to the Version Strategy.
(strategy content path)
spring.resources.chain.strategy.fixed.enabled=false # Enable the fixed Version Strategy.
(version strategy 활성화)
spring.resources.chain.strategy.fixed.paths= # Comma-separated list of patterns to apply to the Version Strategy.
(version strategy path)
spring.resources.chain.strategy.fixed.version= # Version string to use for the Version Strategy.
(version strategy version)
spring.resources.static-locations=classpath:/META-INF/resources/,classpath:/resources/,classpath:/static/,classpath:/public/ # Locations of static resources.
(리소스 static location)
# SPRING SOCIAL (SocialWebAutoConfiguration)
spring.social.auto-connection-views=false # Enable the connection status view for supported providers.
(spring social 활성화)
# SPRING SOCIAL FACEBOOK (FacebookAutoConfiguration)
spring.social.facebook.app-id= # your application's Facebook App ID
(스프링 facebook 연동 id)
spring.social.facebook.app-secret= # your application's Facebook App Secret
(스프링 facebook app secret 속성)
# SPRING SOCIAL LINKEDIN (LinkedInAutoConfiguration)
spring.social.linkedin.app-id= # your application's LinkedIn App ID
(스프링 링크드인 app-id)
spring.social.linkedin.app-secret= # your application's LinkedIn App Secret
(스프링 링크드인 app secret 속성)
# SPRING SOCIAL TWITTER (TwitterAutoConfiguration)
(스프링 트위터 속성)
spring.social.twitter.app-id= # your application's Twitter App ID
spring.social.twitter.app-secret= # your application's Twitter App Secret
# THYMELEAF (ThymeleafAutoConfiguration)
(스프링 THYMELEAF 속성)
(Thymeleaf는 Tiles, FreeMarker, SiteMesh처럼 자바에서 사용할 수 있는 뷰 템플릿 엔진이다. 스프링소스에서 만든건지는 모르겠지만 스프링소스에서 열심히 밀고 있기는 하고 Spring MVC와 통합이 잘 되어 있다.)
spring.thymeleaf.cache=true # Enable template caching.
spring.thymeleaf.check-template-location=true # Check that the templates location exists.
spring.thymeleaf.content-type=text/html # Content-Type value.
spring.thymeleaf.enabled=true # Enable MVC Thymeleaf view resolution.
spring.thymeleaf.encoding=UTF-8 # Template encoding.
spring.thymeleaf.excluded-view-names= # Comma-separated list of view names that should be excluded from resolution.
spring.thymeleaf.mode=HTML5 # Template mode to be applied to templates. See also StandardTemplateModeHandlers.
spring.thymeleaf.prefix=classpath:/templates/ # Prefix that gets prepended to view names when building a URL.
spring.thymeleaf.suffix=.html # Suffix that gets appended to view names when building a URL.
spring.thymeleaf.template-resolver-order= # Order of the template resolver in the chain.
spring.thymeleaf.view-names= # Comma-separated list of view names that can be resolved.
# VELOCITY TEMPLATES (VelocityAutoConfiguration)
(스프링 VELOCITY TEMPLATE 속성)
(Velocity Template Engine은 애플리케이션이나 서블릿 내에서 데이터를 표현하게 만들어 준다.
주로 서블릿 기반의 웹사이트들과 같은 다이나믹한 개발에 사용되는데 Velocity의 템플릿과 자바 코드간의
깔끔한 분리는 모델 2 스타일 Model-View-Controller(MVC) 웹 개발에 대하여 이상적으로 만들어 줄 수 있다.
일반적인 템플릿 엔진들처럼 Velocity는 코드생성, XML 생성과 변환, 그리고 텍스트 스트림 프로세싱과 같은 많은
다른 목적들에도 적합하다.)
spring.velocity.allow-request-override=false # Set whether HttpServletRequest attributes are allowed to override (hide) controller generated model attributes of the same name.
spring.velocity.allow-session-override=false # Set whether HttpSession attributes are allowed to override (hide) controller generated model attributes of the same name.
spring.velocity.cache= # Enable template caching.
spring.velocity.charset=UTF-8 # Template encoding.
spring.velocity.check-template-location=true # Check that the templates location exists.
spring.velocity.content-type=text/html # Content-Type value.
spring.velocity.date-tool-attribute= # Name of the DateTool helper object to expose in the Velocity context of the view.
spring.velocity.enabled=true # Enable MVC view resolution for this technology.
spring.velocity.expose-request-attributes=false # Set whether all request attributes should be added to the model prior to merging with the template.
spring.velocity.expose-session-attributes=false # Set whether all HttpSession attributes should be added to the model prior to merging with the template.
spring.velocity.expose-spring-macro-helpers=true # Set whether to expose a RequestContext for use by Spring's macro library, under the name "springMacroRequestContext".
spring.velocity.number-tool-attribute= # Name of the NumberTool helper object to expose in the Velocity context of the view.
spring.velocity.prefer-file-system-access=true # Prefer file system access for template loading. File system access enables hot detection of template changes.
spring.velocity.prefix= # Prefix that gets prepended to view names when building a URL.
spring.velocity.properties.*= # Additional velocity properties.
spring.velocity.request-context-attribute= # Name of the RequestContext attribute for all views.
spring.velocity.resource-loader-path=classpath:/templates/ # Template path.
spring.velocity.suffix=.vm # Suffix that gets appended to view names when building a URL.
spring.velocity.toolbox-config-location= # Velocity Toolbox config location. For instance `/WEB-INF/toolbox.xml`
spring.velocity.view-names= # White list of view names that can be resolved.
# ----------------------------------------
# SECURITY PROPERTIES
# ----------------------------------------
# SECURITY (SecurityProperties)
(스프링 보안 속성)
security.basic.authorize-mode=role # Security authorize mode to apply.
security.basic.enabled=true # Enable basic authentication.
security.basic.path=/** # Comma-separated list of paths to secure.
security.basic.realm=Spring # HTTP basic realm name.
security.enable-csrf=false # Enable Cross Site Request Forgery support.
security.filter-order=0 # Security filter chain order.
security.filter-dispatcher-types=ASYNC, FORWARD, INCLUDE, REQUEST # Security filter chain dispatcher types.
security.headers.cache=true # Enable cache control HTTP headers.
security.headers.content-type=true # Enable "X-Content-Type-Options" header.
security.headers.frame=true # Enable "X-Frame-Options" header.
security.headers.hsts= # HTTP Strict Transport Security (HSTS) mode (none, domain, all).
security.headers.xss=true # Enable cross site scripting (XSS) protection.
security.ignored= # Comma-separated list of paths to exclude from the default secured paths.
security.require-ssl=false # Enable secure channel for all requests.
security.sessions=stateless # Session creation policy (always, never, if_required, stateless).
security.user.name=user # Default user name.
security.user.password= # Password for the default user name. A random password is logged on startup by default.
security.user.role=USER # Granted roles for the default user name.
# SECURITY OAUTH2 CLIENT (OAuth2ClientProperties
(스프링 OAUTH2 클라이언트 속성)
(외부 사이트와 인증기반의 데이터를 연동할 때 ID, Password를 넘기는 방법은 매우 위험하다.
ID, Password는 그 사용자의 모든 권한을 얻는 것이기 때문에 ID 도용 위험이 크다.
그래서 ID, Password를 사용자 임시 인증을 위한 Token을 제공하는 방식을 사용한다.
그러나 이 방법이 각 서비스마다 제각각이어서 개발자들은 인증 연동을 각 서비스별로 따로 해야 한다.
그러다 보니 표준적인 방법이 필요했고, 그 표준 방법이 OAuth이다.)
security.oauth2.client.client-id= # OAuth2 client id.
security.oauth2.client.client-secret= # OAuth2 client secret. A random secret is generated by default
# SECURITY OAUTH2 RESOURCES (ResourceServerProperties
(스프링 OAUTH2 리소스 속성)
security.oauth2.resource.id= # Identifier of the resource.
security.oauth2.resource.jwt.key-uri= # The URI of the JWT token. Can be set if the value is not available and the key is public.
security.oauth2.resource.jwt.key-value= # The verification key of the JWT token. Can either be a symmetric secret or PEM-encoded RSA public key.
security.oauth2.resource.prefer-token-info=true # Use the token info, can be set to false to use the user info.
security.oauth2.resource.service-id=resource #
security.oauth2.resource.token-info-uri= # URI of the token decoding endpoint.
security.oauth2.resource.token-type= # The token type to send when using the userInfoUri.
security.oauth2.resource.user-info-uri= # URI of the user endpoint.
# SECURITY OAUTH2 SSO (OAuth2SsoProperties
(스프링 OAUTH2 SSO속성)
security.oauth2.sso.filter-order= # Filter order to apply if not providing an explicit WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter
security.oauth2.sso.login-path=/login # Path to the login page, i.e. the one that triggers the redirect to the OAuth2 Authorization Server
# ----------------------------------------
# DATA PROPERTIES
# ----------------------------------------
# FLYWAY (FlywayProperties)
(data flyaway관련 속성)
(데이터베이스 형상관리 툴.
로컬에서 변경한 데이터베이스의 스키마나 데이터를 운영 데이터베이스에 반영하는 것을 누락하는것을 막기 위해 사용한다.
또한 개발 DB와 운영 DB의 스키마를 비교하거나, 운영 DB에 수작업을 가하는 노가다와 위험성을 줄이기 위해 사용한다.
생성한 형상을 새로운 DB에 적용하면 그게 마이그레이션이다.)
flyway.baseline-description= #
flyway.baseline-version=1 # version to start migration
flyway.baseline-on-migrate= #
flyway.check-location=false # Check that migration scripts location exists.
flyway.clean-on-validation-error= #
flyway.enabled=true # Enable flyway.
flyway.encoding= #
flyway.ignore-failed-future-migration= #
flyway.init-sqls= # SQL statements to execute to initialize a connection immediately after obtaining it.
flyway.locations=classpath:db/migration # locations of migrations scripts
flyway.out-of-order= #
flyway.password= # JDBC password if you want Flyway to create its own DataSource
flyway.placeholder-prefix= #
flyway.placeholder-replacement= #
flyway.placeholder-suffix= #
flyway.placeholders.*= #
flyway.schemas= # schemas to update
flyway.sql-migration-prefix=V #
flyway.sql-migration-separator= #
flyway.sql-migration-suffix=.sql #
flyway.table= #
flyway.url= # JDBC url of the database to migrate. If not set, the primary configured data source is used.
flyway.user= # Login user of the database to migrate.
flyway.validate-on-migrate= #
# LIQUIBASE (LiquibaseProperties)
(LIQUIBASE 속성)
(데이터베이스 변경 관리를 체계적으로 자동화해 주는 open source(LGPL)로 LiquiBase)
liquibase.change-log=classpath:/db/changelog/db.changelog-master.yaml # Change log configuration path.
liquibase.check-change-log-location=true # Check the change log location exists.
liquibase.contexts= # Comma-separated list of runtime contexts to use.
liquibase.default-schema= # Default database schema.
liquibase.drop-first=false # Drop the database schema first.
liquibase.enabled=true # Enable liquibase support.
liquibase.labels= # Comma-separated list of runtime labels to use.
liquibase.parameters.*= # Change log parameters.
liquibase.password= # Login password of the database to migrate.
liquibase.url= # JDBC url of the database to migrate. If not set, the primary configured data source is used.
liquibase.user= # Login user of the database to migrate.
# DAO (PersistenceExceptionTranslationAutoConfiguration)
(스프링 DAO관련 속성)
spring.dao.exceptiontranslation.enabled=true # Enable the PersistenceExceptionTranslationPostProcessor.
# CASSANDRA (CassandraProperties)
(CASSANDRA 속성)
(카산드라는 구글의 BigTable 컬럼 기반의 데이타 모델과 FaceBook에서 만든 Dynamo의 분산 모델을 기반으로 하여 제작되어 Facebook에 의해 2008년에 아파치 오픈소스로 공개된 분산 데이타 베이스 입니다.)
spring.data.cassandra.cluster-name= # Name of the Cassandra cluster.
spring.data.cassandra.compression= # Compression supported by the Cassandra binary protocol.
spring.data.cassandra.connect-timeout-millis= # Socket option: connection time out.
spring.data.cassandra.consistency-level= # Queries consistency level.
spring.data.cassandra.contact-points=localhost # Comma-separated list of cluster node addresses.
spring.data.cassandra.fetch-size= # Queries default fetch size.
spring.data.cassandra.keyspace-name= # Keyspace name to use.
spring.data.cassandra.load-balancing-policy= # Class name of the load balancing policy.
spring.data.cassandra.port= # Port of the Cassandra server.
spring.data.cassandra.password= # Login password of the server.
spring.data.cassandra.read-timeout-millis= # Socket option: read time out.
spring.data.cassandra.reconnection-policy= # Reconnection policy class.
spring.data.cassandra.retry-policy= # Class name of the retry policy.
spring.data.cassandra.serial-consistency-level= # Queries serial consistency level.
spring.data.cassandra.ssl=false # Enable SSL support.
spring.data.cassandra.username= # Login user of the server.
# ELASTICSEARCH (ElasticsearchProperties)
(ELASTICSEARCH 관련 속성)
(elasticsearch는 Shay Banon이 Lucene을 바탕으로 개발한 분산 검색엔진입니다.
설치와 서버 확장이 매우 편리하기 때문에 개발하고 있는 시스템에 검색 기능이 필요하다면 elasticsearch를 적용하는 것을 권장하고 싶습니다.
분산 시스템이기 때문에 검색 대상 용량이 증가했을 때 대응하기가 무척 수월하다는 것이 장점입니다.)
spring.data.elasticsearch.cluster-name=elasticsearch # Elasticsearch cluster name.
spring.data.elasticsearch.cluster-nodes= # Comma-separated list of cluster node addresses. If not specified, starts a client node.
spring.data.elasticsearch.properties.*= # Additional properties used to configure the client.
spring.data.elasticsearch.repositories.enabled=true # Enable Elasticsearch repositories.
# MONGODB (MongoProperties)
(스프링 데이터 mongodb속성)
spring.data.mongodb.authentication-database= # Authentication database name.
spring.data.mongodb.database=test # Database name.
spring.data.mongodb.field-naming-strategy= # Fully qualified name of the FieldNamingStrategy to use.
spring.data.mongodb.grid-fs-database= # GridFS database name.
spring.data.mongodb.host=localhost # Mongo server host.
spring.data.mongodb.password= # Login password of the mongo server.
spring.data.mongodb.port=27017 # Mongo server port.
spring.data.mongodb.repositories.enabled=true # Enable Mongo repositories.
spring.data.mongodb.uri=mongodb://localhost/test # Mongo database URI. When set, host and port are ignored.
spring.data.mongodb.username= # Login user of the mongo server.
# DATA REST (RepositoryRestProperties)
(DATA REST 관련 속성)
(Spring에서 REST 서비스를 만들 때 가장 빠르고 효율적으로 만들 수 있는 기술이다.)
spring.data.rest.base-path= # Base path to be used by Spring Data REST to expose repository resources.
spring.data.rest.default-page-size= # Default size of pages.
spring.data.rest.enable-enum-translation= # Enable enum value translation via the Spring Data REST default resource bundle.
spring.data.rest.limit-param-name= # Name of the URL query string parameter that indicates how many results to return at once.
spring.data.rest.max-page-size= # Maximum size of pages.
spring.data.rest.page-param-name= # Name of the URL query string parameter that indicates what page to return.
spring.data.rest.return-body-on-create= # Return a response body after creating an entity.
spring.data.rest.return-body-on-update= # Return a response body after updating an entity.
spring.data.rest.sort-param-name= # Name of the URL query string parameter that indicates what direction to sort results.
# SOLR (SolrProperties)
(SOLR관련 속성)
(Solr는 단독 애플리케이션 서버 형태로 작동하며, REST 형식의 API를 제공한다.
문서들은 HTTP를 이용해서 XML, JSON, CSV 혹은 바이너리 형태등으로 색인요청을 할 수 있다.
검색 역시 HTTP GET 으로 요청하며, 검색결과는 XML, JSON, CSV, 바이너리 형태로 가져올 수 있다.)
spring.data.solr.host=http://127.0.0.1:8983/solr # Solr host. Ignored if "zk-host" is set.
spring.data.solr.repositories.enabled=true # Enable Solr repositories.
spring.data.solr.zk-host= # ZooKeeper host address in the form HOST:PORT.
# DATASOURCE (DataSourceAutoConfiguration & DataSourceProperties)
(DATASOURCE관련 속성)
(jdbc를 사용하여 db에 접속하기 위해서는 드라이버를 로드하고 db에 접속하여 connection 객체를 받아와야 한다.
이런식이면 db에 쿼리를 보낼때 마다 드라이버를 로드하고 커넥션을 생성하고 닫게되는데 커넥션을 생성하고 다는데
시간이 소모되기에 동시접속자가 많은 사이트의 경우 전체의 성능을 낮추는 원인이 된다.
(드라이버도 한번만 로드하면 되는데 불필요하게 여러번 로드하게 된다)
이런 문제를 해결하기 위해 "커넥션 풀"을 사용하는데 javax.sql.DataSource 를 사용하면 된다.)
spring.datasource.continue-on-error=false # Do not stop if an error occurs while initializing the database.
spring.datasource.data= # Data (DML) script resource reference.
spring.datasource.driver-class-name= # Fully qualified name of the JDBC driver. Auto-detected based on the URL by default.
spring.datasource.initialize=true # Populate the database using 'data.sql'.
spring.datasource.jmx-enabled=false # Enable JMX support (if provided by the underlying pool).
spring.datasource.jndi-name= # JNDI location of the datasource. Class, url, username & password are ignored when set.
spring.datasource.max-active= # For instance 100
spring.datasource.max-idle= # For instance 8
spring.datasource.max-wait=
spring.datasource.min-evictable-idle-time-millis=
spring.datasource.min-idle=8
spring.datasource.name=testdb # Name of the datasource.
spring.datasource.password= # Login password of the database.
spring.datasource.platform=all # Platform to use in the schema resource (schema-${platform}.sql).
spring.datasource.schema= # Schema (DDL) script resource reference.
spring.datasource.separator=; # Statement separator in SQL initialization scripts.
spring.datasource.sql-script-encoding= # SQL scripts encoding.
spring.datasource.test-on-borrow= # For instance `false`
spring.datasource.test-on-return= # For instance `false`
spring.datasource.test-while-idle= #
spring.datasource.time-between-eviction-runs-millis= 1
spring.datasource.type= # Fully qualified name of the connection pool implementation to use. By default, it is auto-detected from the classpath.
spring.datasource.url= # JDBC url of the database.
spring.datasource.username=
spring.datasource.validation-query=
# H2 Web Console (H2ConsoleProperties)
(H2 Web Console 관련 속성)
(H2 DBMS는 HSQLDB의 후속 버젼으로 많은 기능과 CONSOL을 제공하여 기존의 HSQLDB 보다 쉬게 이용 할수 있다.)
spring.h2.console.enabled=false # Enable the console.
spring.h2.console.path=/h2-console # Path at which the console will be available.
# JOOQ (JooqAutoConfiguration)
(JOOQ관련 속성)
spring.jooq.sql-dialect= # SQLDialect JOOQ used when communicating with the configured datasource. For instance `POSTGRES`
# JPA (JpaBaseConfiguration, HibernateJpaAutoConfiguration)
(JPA는 java persistence api로 데이터베이스를 객최화 하여 연동, 관리가 가능하다.)
spring.data.jpa.repositories.enabled=true # Enable JPA repositories.
(jpa 레포지토리 활성화)
spring.jpa.database= # Target database to operate on, auto-detected by default. Can be alternatively set using the "databasePlatform" property.
(사용할 jpa database 종류 선언)
spring.jpa.database-platform= # Name of the target database to operate on, auto-detected by default. Can be alternatively set using the "Database" enum.
(jpa 플랫폼 이름)
spring.jpa.generate-ddl=false # Initialize the schema on startup.
(시작시 스키마 초기화 여부)
spring.jpa.hibernate.ddl-auto= # DDL mode. This is actually a shortcut for the "hibernate.hbm2ddl.auto" property. Default to "create-drop" when using an embedded database, "none" otherwise.
(ddl mode 여부)
spring.jpa.hibernate.naming-strategy= # Naming strategy fully qualified name.
(Qualified name 이름)
spring.jpa.open-in-view=true # Register OpenEntityManagerInViewInterceptor. Binds a JPA EntityManager to the thread for the entire processing of the request.
(jpa 이름)
spring.jpa.properties.*= # Additional native properties to set on the JPA provider.
(jpa 속성)
spring.jpa.show-sql=false # Enable logging of SQL statements.
(로깅에 sql statement를 찍을 것인지 여부)
# JTA (JtaAutoConfiguration)
(JTA관련 속성)
(JTA(Java Transaction API)은 플랫폼마다 상이한 트랜잭션 매니저들과 어플리케이션들이 상호작용할 수 있는 인터페이스를 정의하고 있다.)
spring.jta.log-dir= # Transaction logs directory.
# ATOMIKOS
(ATOMIKOS관련 속성)
spring.jta.checkpoint-interval=500 # Interval between checkpoints.
spring.jta.console-file-count=1 # Number of debug logs files that can be created.
spring.jta.console-file-limit=-1 # How many bytes can be stored at most in debug logs files.
spring.jta.console-file-name=tm.out # Debug logs file name.
spring.jta.console-log-level= # Console log level.
spring.jta.default-jta-timeout=10000 # Default timeout for JTA transactions.
spring.jta.enable-logging=true # Enable disk logging.
spring.jta.force-shutdown-on-vm-exit=false # Specify if a VM shutdown should trigger forced shutdown of the transaction core.
spring.jta.log-base-dir= # Directory in which the log files should be stored.
spring.jta.log-base-name=tmlog # Transactions log file base name.
spring.jta.max-actives=50 # Maximum number of active transactions.
spring.jta.max-timeout=300000 # Maximum timeout (in milliseconds) that can be allowed for transactions.
spring.jta.output-dir= # Directory in which to store the debug log files.
spring.jta.serial-jta-transactions=true # Specify if sub-transactions should be joined when possible.
spring.jta.service= # Transaction manager implementation that should be started.
spring.jta.threaded-two-phase-commit=true # Use different (and concurrent) threads for two-phase commit on the participating resources.
spring.jta.transaction-manager-unique-name= # Transaction manager's unique name.
spring.jta.atomikos.connectionfactory.borrow-connection-timeout=30 # Timeout, in seconds, for borrowing connections from the pool.
spring.jta.atomikos.connectionfactory.ignore-session-transacted-flag=true # Whether or not to ignore the transacted flag when creating session.
spring.jta.atomikos.connectionfactory.local-transaction-mode=false # Whether or not local transactions are desired.
spring.jta.atomikos.connectionfactory.maintenance-interval=60 # The time, in seconds, between runs of the pool's maintenance thread.
spring.jta.atomikos.connectionfactory.max-idle-time=60 # The time, in seconds, after which connections are cleaned up from the pool.
spring.jta.atomikos.connectionfactory.max-lifetime=0 # The time, in seconds, that a connection can be pooled for before being destroyed. 0 denotes no limit.
spring.jta.atomikos.connectionfactory.max-pool-size=1 # The maximum size of the pool.
spring.jta.atomikos.connectionfactory.min-pool-size=1 # The minimum size of the pool.
spring.jta.atomikos.connectionfactory.reap-timeout=0 # The reap timeout, in seconds, for borrowed connections. 0 denotes no limit.
spring.jta.atomikos.connectionfactory.unique-resource-name=jmsConnectionFactory # The unique name used to identify the resource during recovery.
spring.jta.atomikos.datasource.borrow-connection-timeout=30 # Timeout, in seconds, for borrowing connections from the pool.
spring.jta.atomikos.datasource.default-isolation-level= # Default isolation level of connections provided by the pool.
spring.jta.atomikos.datasource.login-timeout= # Timeout, in seconds, for establishing a database connection.
spring.jta.atomikos.datasource.maintenance-interval=60 # The time, in seconds, between runs of the pool's maintenance thread.
spring.jta.atomikos.datasource.max-idle-time=60 # The time, in seconds, after which connections are cleaned up from the pool.
spring.jta.atomikos.datasource.max-lifetime=0 # The time, in seconds, that a connection can be pooled for before being destroyed. 0 denotes no limit.
spring.jta.atomikos.datasource.max-pool-size=1 # The maximum size of the pool.
spring.jta.atomikos.datasource.min-pool-size=1 # The minimum size of the pool.
spring.jta.atomikos.datasource.reap-timeout=0 # The reap timeout, in seconds, for borrowed connections. 0 denotes no limit.
spring.jta.atomikos.datasource.test-query= # SQL query or statement used to validate a connection before returning it.
spring.jta.atomikos.datasource.unique-resource-name=dataSource # The unique name used to identify the resource during recovery.
# BITRONIX
(BITRONIX관련 속성)
spring.jta.allow-multiple-lrc=false # Allow multiple LRC resources to be enlisted into the same transaction.
spring.jta.asynchronous2-pc=false # Enable asynchronously execution of two phase commit.
spring.jta.background-recovery-interval-seconds=60 # Interval in seconds at which to run the recovery process in the background.
spring.jta.current-node-only-recovery=true # Recover only the current node.
spring.jta.debug-zero-resource-transaction=false # Log the creation and commit call stacks of transactions executed without a single enlisted resource.
spring.jta.default-transaction-timeout=60 # Default transaction timeout in seconds.
spring.jta.disable-jmx=false # Enable JMX support.
spring.jta.exception-analyzer= # Set the fully qualified name of the exception analyzer implementation to use.
spring.jta.filter-log-status=false # Enable filtering of logs so that only mandatory logs are written.
spring.jta.force-batching-enabled=true # Set if disk forces are batched.
spring.jta.forced-write-enabled=true # Set if logs are forced to disk.
spring.jta.graceful-shutdown-interval=60 # Maximum amount of seconds the TM will wait for transactions to get done before aborting them at shutdown time.
spring.jta.jndi-transaction-synchronization-registry-name= # JNDI name of the TransactionSynchronizationRegistry.
spring.jta.jndi-user-transaction-name= # JNDI name of the UserTransaction.
spring.jta.journal=disk # Name of the journal. Can be 'disk', 'null' or a class name.
spring.jta.log-part1-filename=btm1.tlog # Name of the first fragment of the journal.
spring.jta.log-part2-filename=btm2.tlog # Name of the second fragment of the journal.
spring.jta.max-log-size-in-mb=2 # Maximum size in megabytes of the journal fragments.
spring.jta.resource-configuration-filename= # ResourceLoader configuration file name.
spring.jta.server-id= # ASCII ID that must uniquely identify this TM instance. Default to the machine's IP address.
spring.jta.skip-corrupted-logs=false # Skip corrupted transactions log entries.
spring.jta.warn-about-zero-resource-transaction=true # Log a warning for transactions executed without a single enlisted resource.
spring.jta.bitronix.connectionfactory.acquire-increment=1 # Number of connections to create when growing the pool.
spring.jta.bitronix.connectionfactory.acquisition-interval=1 # Time, in seconds, to wait before trying to acquire a connection again after an invalid connection was acquired.
spring.jta.bitronix.connectionfactory.acquisition-timeout=30 # Timeout, in seconds, for acquiring connections from the pool.
spring.jta.bitronix.connectionfactory.allow-local-transactions=true # Whether or not the transaction manager should allow mixing XA and non-XA transactions.
spring.jta.bitronix.connectionfactory.apply-transaction-timeout=false # Whether or not the transaction timeout should be set on the XAResource when it is enlisted.
spring.jta.bitronix.connectionfactory.automatic-enlisting-enabled=true # Whether or not resources should be enlisted and delisted automatically.
spring.jta.bitronix.connectionfactory.cache-producers-consumers=true # Whether or not produces and consumers should be cached.
spring.jta.bitronix.connectionfactory.defer-connection-release=true # Whether or not the provider can run many transactions on the same connection and supports transaction interleaving.
spring.jta.bitronix.connectionfactory.ignore-recovery-failures=false # Whether or not recovery failures should be ignored.
spring.jta.bitronix.connectionfactory.max-idle-time=60 # The time, in seconds, after which connections are cleaned up from the pool.
spring.jta.bitronix.connectionfactory.max-pool-size=10 # The maximum size of the pool. 0 denotes no limit.
spring.jta.bitronix.connectionfactory.min-pool-size=0 # The minimum size of the pool.
spring.jta.bitronix.connectionfactory.password= # The password to use to connect to the JMS provider.
spring.jta.bitronix.connectionfactory.share-transaction-connections=false # Whether or not connections in the ACCESSIBLE state can be shared within the context of a transaction.
spring.jta.bitronix.connectionfactory.test-connections=true # Whether or not connections should be tested when acquired from the pool.
spring.jta.bitronix.connectionfactory.two-pc-ordering-position=1 # The position that this resource should take during two-phase commit (always first is Integer.MIN_VALUE, always last is Integer.MAX_VALUE).
spring.jta.bitronix.connectionfactory.unique-name=jmsConnectionFactory # The unique name used to identify the resource during recovery.
spring.jta.bitronix.connectionfactory.use-tm-join=true Whether or not TMJOIN should be used when starting XAResources.
spring.jta.bitronix.connectionfactory.user= # The user to use to connect to the JMS provider.
spring.jta.bitronix.datasource.acquire-increment=1 # Number of connections to create when growing the pool.
spring.jta.bitronix.datasource.acquisition-interval=1 # Time, in seconds, to wait before trying to acquire a connection again after an invalid connection was acquired.
spring.jta.bitronix.datasource.acquisition-timeout=30 # Timeout, in seconds, for acquiring connections from the pool.
spring.jta.bitronix.datasource.allow-local-transactions=true # Whether or not the transaction manager should allow mixing XA and non-XA transactions.
spring.jta.bitronix.datasource.apply-transaction-timeout=false # Whether or not the transaction timeout should be set on the XAResource when it is enlisted.
spring.jta.bitronix.datasource.automatic-enlisting-enabled=true # Whether or not resources should be enlisted and delisted automatically.
spring.jta.bitronix.datasource.cursor-holdability= # The default cursor holdability for connections.
spring.jta.bitronix.datasource.defer-connection-release=true # Whether or not the database can run many transactions on the same connection and supports transaction interleaving.
spring.jta.bitronix.datasource.enable-jdbc4-connection-test= # Whether or not Connection.isValid() is called when acquiring a connection from the pool.
spring.jta.bitronix.datasource.ignore-recovery-failures=false # Whether or not recovery failures should be ignored.
spring.jta.bitronix.datasource.isolation-level= # The default isolation level for connections.
spring.jta.bitronix.datasource.local-auto-commit= # The default auto-commit mode for local transactions.
spring.jta.bitronix.datasource.login-timeout= # Timeout, in seconds, for establishing a database connection.
spring.jta.bitronix.datasource.max-idle-time=60 # The time, in seconds, after which connections are cleaned up from the pool.
spring.jta.bitronix.datasource.max-pool-size=10 # The maximum size of the pool. 0 denotes no limit.
spring.jta.bitronix.datasource.min-pool-size=0 # The minimum size of the pool.
spring.jta.bitronix.datasource.prepared-statement-cache-size=0 # The target size of the prepared statement cache. 0 disables the cache.
spring.jta.bitronix.datasource.share-transaction-connections=false # Whether or not connections in the ACCESSIBLE state can be shared within the context of a transaction.
spring.jta.bitronix.datasource.test-query= # SQL query or statement used to validate a connection before returning it.
spring.jta.bitronix.datasource.two-pc-ordering-position=1 # The position that this resource should take during two-phase commit (always first is Integer.MIN_VALUE, always last is Integer.MAX_VALUE).
spring.jta.bitronix.datasource.unique-name=dataSource # The unique name used to identify the resource during recovery.
spring.jta.bitronix.datasource.use-tm-join=true Whether or not TMJOIN should be used when starting XAResources.
# EMBEDDED MONGODB (EmbeddedMongoProperties)
(EMBEDDED mongodb 속성)
spring.mongodb.embedded.features=SYNC_DELAY # Comma-separated list of features to enable.
spring.mongodb.embedded.version=2.6.10 # Version of Mongo to use.
# REDIS (RedisProperties)
(REDIS 관련 속성)
(Redis는 "REmote DIctionary System"의 약자로 메모리 기반의 Key/Value Store 이다.
Cassandra나 HBase와 같이 NoSQL DBMS로 분류되기도 하고, memcached와 같은 In memory 솔루션으로 분리되기도 한다.)
spring.redis.database=0 # Database index used by the connection factory.
spring.redis.host=localhost # Redis server host.
spring.redis.password= # Login password of the redis server.
spring.redis.pool.max-active=8 # Max number of connections that can be allocated by the pool at a given time. Use a negative value for no limit.
spring.redis.pool.max-idle=8 # Max number of "idle" connections in the pool. Use a negative value to indicate an unlimited number of idle connections.
spring.redis.pool.max-wait=-1 # Maximum amount of time (in milliseconds) a connection allocation should block before throwing an exception when the pool is exhausted. Use a negative value to block indefinitely.
spring.redis.pool.min-idle=0 # Target for the minimum number of idle connections to maintain in the pool. This setting only has an effect if it is positive.
spring.redis.port=6379 # Redis server port.
spring.redis.sentinel.master= # Name of Redis server.
spring.redis.sentinel.nodes= # Comma-separated list of host:port pairs.
spring.redis.timeout=0 # Connection timeout in milliseconds.
# ----------------------------------------
# INTEGRATION PROPERTIES
# ----------------------------------------
# ACTIVEMQ (ActiveMQProperties)
(ACTIVEMQ관련 속성)
(Apache ActiveMQ는 가장 유명하고 강력한 오픈 소스 메시지 브로커입니다. Apache ActiveMQ는 빠르고, 다양한 언어 환경의 클라이언트들과 프로토콜을 지원하며, JMS 1.1과 J2EE 1.4를 지원하는 동시에 매우 고급 기능들을 지원하며 Apache 2.0 라이센스에 의해 릴리즈 됩니다.)
spring.activemq.broker-url= # URL of the ActiveMQ broker. Auto-generated by default. For instance `tcp://localhost:61616`
spring.activemq.in-memory=true # Specify if the default broker URL should be in memory. Ignored if an explicit broker has been specified.
spring.activemq.password= # Login password of the broker.
spring.activemq.pooled=false # Specify if a PooledConnectionFactory should be created instead of a regular ConnectionFactory.
spring.activemq.user= # Login user of the broker.
# ARTEMIS (ArtemisProperties)
(ARTEMIS관련 속성)
spring.artemis.embedded.cluster-password= # Cluster password. Randomly generated on startup by default.
spring.artemis.embedded.data-directory= # Journal file directory. Not necessary if persistence is turned off.
spring.artemis.embedded.enabled=true # Enable embedded mode if the Artemis server APIs are available.
spring.artemis.embedded.persistent=false # Enable persistent store.
spring.artemis.embedded.queues= # Comma-separated list of queues to create on startup.
spring.artemis.embedded.server-id= # Server id. By default, an auto-incremented counter is used.
spring.artemis.embedded.topics= # Comma-separated list of topics to create on startup.
spring.artemis.host=localhost # Artemis broker host.
spring.artemis.mode= # Artemis deployment mode, auto-detected by default. Can be explicitly set to "native" or "embedded".
spring.artemis.port=61616 # Artemis broker port.
# SPRING BATCH (BatchProperties)
(SPRING batch 관련 속성)
spring.batch.initializer.enabled=true # Create the required batch tables on startup if necessary.
(스프링 batch 초기화 활성화)
spring.batch.job.enabled=true # Execute all Spring Batch jobs in the context on startup.
(스프링 batch job 활성화)
spring.batch.job.names= # Comma-separated list of job names to execute on startup (For instance `job1,job2`). By default, all Jobs found in the context are executed.
(시작시에 수행할 스프링 batch job 이름들 입력)
spring.batch.schema=classpath:org/springframework/batch/core/schema-@@platform@@.sql # Path to the SQL file to use to initialize the database schema.
(spring batch schema)
spring.batch.table-prefix= # Table prefix for all the batch meta-data tables.
(spring batch table prefix)
# HORNETQ (HornetQProperties)
(HORNETQ 관련 속성)
spring.hornetq.embedded.cluster-password= # Cluster password. Randomly generated on startup by default.
spring.hornetq.embedded.data-directory= # Journal file directory. Not necessary if persistence is turned off.
spring.hornetq.embedded.enabled=true # Enable embedded mode if the HornetQ server APIs are available.
spring.hornetq.embedded.persistent=false # Enable persistent store.
spring.hornetq.embedded.queues= # Comma-separated list of queues to create on startup.
spring.hornetq.embedded.server-id= # Server id. By default, an auto-incremented counter is used.
spring.hornetq.embedded.topics= # Comma-separated list of topics to create on startup.
spring.hornetq.host=localhost # HornetQ broker host.
spring.hornetq.mode= # HornetQ deployment mode, auto-detected by default. Can be explicitly set to "native" or "embedded".
spring.hornetq.port=5445 # HornetQ broker port.
# JMS (JmsProperties)
(JMS 관련 속성)
(스프링은 JDBC API를 통합했듯이 JMS API도 사용하기 쉽게 JMS 통합 프레임워크를 제공한다. JMS는 기능적으로 대략 두 부분으로 나눌 수 있는데 메시지의 생산(production)과 소비(consumption)이다. JmsTemplate 클래스는 메시지 생산과 동기적인 메시지 수신에 사용한다. Java EE의 메시지주도 빈(bean) 방식과 유사한 비동기적인 수신에 대해서 스프링은 메시지주도 POJO(MDP, Message-Driven POJOs)를 생성하는데 사용하는 다수의 메시지 리스너 컨테이너를 제공한다.)
spring.jms.jndi-name= # Connection factory JNDI name. When set, takes precedence to others connection factory auto-configurations.
spring.jms.listener.acknowledge-mode= # Acknowledge mode of the container. By default, the listener is transacted with automatic acknowledgment.
spring.jms.listener.auto-startup=true # Start the container automatically on startup.
spring.jms.listener.concurrency= # Minimum number of concurrent consumers.
spring.jms.listener.max-concurrency= # Maximum number of concurrent consumers.
spring.jms.pub-sub-domain=false # Specify if the default destination type is topic.
# RABBIT (RabbitProperties)
(RABBIT관련 속성)
spring.rabbitmq.addresses= # Comma-separated list of addresses to which the client should connect to.
spring.rabbitmq.dynamic=true # Create an AmqpAdmin bean.
spring.rabbitmq.host=localhost # RabbitMQ host.
spring.rabbitmq.listener.acknowledge-mode= # Acknowledge mode of container.
spring.rabbitmq.listener.auto-startup=true # Start the container automatically on startup.
spring.rabbitmq.listener.concurrency= # Minimum number of consumers.
spring.rabbitmq.listener.max-concurrency= # Maximum number of consumers.
spring.rabbitmq.listener.prefetch= # Number of messages to be handled in a single request. It should be greater than or equal to the transaction size (if used).
spring.rabbitmq.listener.transaction-size= # Number of messages to be processed in a transaction. For best results it should be less than or equal to the prefetch count.
spring.rabbitmq.password= # Login to authenticate against the broker.
spring.rabbitmq.port=5672 # RabbitMQ port.
spring.rabbitmq.requested-heartbeat= # Requested heartbeat timeout, in seconds; zero for none.
spring.rabbitmq.ssl.enabled=false # Enable SSL support.
spring.rabbitmq.ssl.key-store= # Path to the key store that holds the SSL certificate.
spring.rabbitmq.ssl.key-store-password= # Password used to access the key store.
spring.rabbitmq.ssl.trust-store= # Trust store that holds SSL certificates.
spring.rabbitmq.ssl.trust-store-password= # Password used to access the trust store.
spring.rabbitmq.ssl.algorithm= # SSL algorithm to use. By default configure by the rabbit client library.
spring.rabbitmq.username= # Login user to authenticate to the broker.
spring.rabbitmq.virtual-host= # Virtual host to use when connecting to the broker.
# ----------------------------------------
# ACTUATOR PROPERTIES
# ----------------------------------------
# ENDPOINTS (AbstractEndpoint subclasses)
(ENDPOINTS 관련 속성)
endpoints.enabled=true # Enable endpoints.
endpoints.sensitive= # Default endpoint sensitive setting.
endpoints.actuator.enabled=true # Enable the endpoint.
endpoints.actuator.path= # Endpoint URL path.
endpoints.actuator.sensitive=false # Enable security on the endpoint.
endpoints.autoconfig.enabled= # Enable the endpoint.
endpoints.autoconfig.id= # Endpoint identifier.
endpoints.autoconfig.sensitive= # Mark if the endpoint exposes sensitive information.
endpoints.beans.enabled= # Enable the endpoint.
endpoints.beans.id= # Endpoint identifier.
endpoints.beans.sensitive= # Mark if the endpoint exposes sensitive information.
endpoints.configprops.enabled= # Enable the endpoint.
endpoints.configprops.id= # Endpoint identifier.
endpoints.configprops.keys-to-sanitize=password,secret,key,.*credentials.*,vcap_services # Keys that should be sanitized. Keys can be simple strings that the property ends with or regex expressions.
endpoints.configprops.sensitive= # Mark if the endpoint exposes sensitive information.
endpoints.docs.curies.enabled=false # Enable the curie generation.
endpoints.docs.enabled=true # Enable actuator docs endpoint.
endpoints.docs.path=/docs #
endpoints.docs.sensitive=false #
endpoints.dump.enabled= # Enable the endpoint.
endpoints.dump.id= # Endpoint identifier.
endpoints.dump.sensitive= # Mark if the endpoint exposes sensitive information.
endpoints.env.enabled= # Enable the endpoint.
endpoints.env.id= # Endpoint identifier.
endpoints.env.keys-to-sanitize=password,secret,key,.*credentials.*,vcap_services # Keys that should be sanitized. Keys can be simple strings that the property ends with or regex expressions.
endpoints.env.sensitive= # Mark if the endpoint exposes sensitive information.
endpoints.flyway.enabled= # Enable the endpoint.
endpoints.flyway.id= # Endpoint identifier.
endpoints.flyway.sensitive= # Mark if the endpoint exposes sensitive information.
endpoints.health.enabled= # Enable the endpoint.
endpoints.health.id= # Endpoint identifier.
endpoints.health.mapping.*= # Mapping of health statuses to HttpStatus codes. By default, registered health statuses map to sensible defaults (i.e. UP maps to 200).
endpoints.health.sensitive= # Mark if the endpoint exposes sensitive information.
endpoints.health.time-to-live=1000 # Time to live for cached result, in milliseconds.
endpoints.info.enabled= # Enable the endpoint.
endpoints.info.id= # Endpoint identifier.
endpoints.info.sensitive= # Mark if the endpoint exposes sensitive information.
endpoints.jolokia.enabled=true # Enable Jolokia endpoint.
endpoints.jolokia.path=/jolokia # Endpoint URL path.
endpoints.jolokia.sensitive=true # Enable security on the endpoint.
endpoints.liquibase.enabled= # Enable the endpoint.
endpoints.liquibase.id= # Endpoint identifier.
endpoints.liquibase.sensitive= # Mark if the endpoint exposes sensitive information.
endpoints.logfile.enabled=true # Enable the endpoint.
endpoints.logfile.path=/logfile # Endpoint URL path.
endpoints.logfile.sensitive=true # Enable security on the endpoint.
endpoints.mappings.enabled= # Enable the endpoint.
endpoints.mappings.id= # Endpoint identifier.
endpoints.mappings.sensitive= # Mark if the endpoint exposes sensitive information.
endpoints.metrics.enabled= # Enable the endpoint.
endpoints.metrics.filter.enabled=true # Enable the metrics servlet filter.
endpoints.metrics.id= # Endpoint identifier.
endpoints.metrics.sensitive= # Mark if the endpoint exposes sensitive information.
endpoints.shutdown.enabled= # Enable the endpoint.
endpoints.shutdown.id= # Endpoint identifier.
endpoints.shutdown.sensitive= # Mark if the endpoint exposes sensitive information.
endpoints.trace.enabled= # Enable the endpoint.
endpoints.trace.id= # Endpoint identifier.
endpoints.trace.sensitive= # Mark if the endpoint exposes sensitive information.
# ENDPOINTS CORS CONFIGURATION (EndpointCorsProperties)
(ENDPOINTS 속성)
endpoints.cors.allow-credentials= # Set whether credentials are supported. When not set, credentials are not supported.
endpoints.cors.allowed-headers= # Comma-separated list of headers to allow in a request. '*' allows all headers.
endpoints.cors.allowed-methods=GET # Comma-separated list of methods to allow. '*' allows all methods.
endpoints.cors.allowed-origins= # Comma-separated list of origins to allow. '*' allows all origins. When not set, CORS support is disabled.
endpoints.cors.exposed-headers= # Comma-separated list of headers to include in a response.
endpoints.cors.max-age=1800 # How long, in seconds, the response from a pre-flight request can be cached by clients.
# JMX ENDPOINT (EndpointMBeanExportProperties)
(JMX endpoint 관련 속성)
endpoints.jmx.domain= # JMX domain name. Initialized with the value of 'spring.jmx.default-domain' if set.
endpoints.jmx.enabled=true # Enable JMX export of all endpoints.
endpoints.jmx.static-names= # Additional static properties to append to all ObjectNames of MBeans representing Endpoints.
endpoints.jmx.unique-names=false # Ensure that ObjectNames are modified in case of conflict.
# JOLOKIA (JolokiaProperties)
(JOLOKIA 관련 속성)
jolokia.config.*= # See Jolokia manual
# MANAGEMENT HTTP SERVER (ManagementServerProperties)
(HTTP 서버 관련 management 속성)
management.add-application-context-header=true # Add the "X-Application-Context" HTTP header in each response.
management.address= # Network address that the management endpoints should bind to.
management.context-path= # Management endpoint context-path. For instance `/actuator`
management.port= # Management endpoint HTTP port. Use the same port as the application by default.
management.security.enabled=true # Enable security.
management.security.role=ADMIN # Role required to access the management endpoint.
management.security.sessions=stateless # Session creating policy to use (always, never, if_required, stateless).
# HEALTH INDICATORS (previously health.*)
(spring 상태 관련 속성 - )
management.health.db.enabled=true # Enable database health check.
(데이터베이스 상태 체크 활성화)
management.health.defaults.enabled=true # Enable default health indicators.
(상테 인디케이터 활성화)
management.health.diskspace.enabled=true # Enable disk space health check.
(디스크 공간 상태 활성화)
management.health.diskspace.path= # Path used to compute the available disk space.
(디스크 공간 관련 path)
management.health.diskspace.threshold=0 # Minimum disk space that should be available, in bytes.
(디스크 공간 minimum threshold)
management.health.elasticsearch.enabled=true # Enable elasticsearch health check.
(엘라스틱 서치 상태 체크 활성화)
management.health.elasticsearch.indices= # Comma-separated index names.
(엘라스틱 index name)
management.health.elasticsearch.response-timeout=100 # The time, in milliseconds, to wait for a response from the cluster.
(엘라스틱 response timeout설정)
management.health.jms.enabled=true # Enable JMS health check.
(java message service 상태 체크 활성화)
management.health.mail.enabled=true # Enable Mail health check.
(mail 상태 체크 활성화)
management.health.mongo.enabled=true # Enable MongoDB health check.
(mongodb 상태 체크 활성화)
management.health.rabbit.enabled=true # Enable RabbitMQ health check.
(rabbitMQ 상태 체크 활성화)
management.health.redis.enabled=true # Enable Redis health check.
(redis 상태 체크 활성화)
management.health.solr.enabled=true # Enable Solr health check.
(solr 상태 체크 활성화)
management.health.status.order=DOWN, OUT_OF_SERVICE, UNKNOWN, UP # Comma-separated list of health statuses in order of severity.
(health status 관련 속성)
# TRACING ((TraceProperties)
management.trace.include=request-headers,response-headers,errors # Items to be included in the trace.
(트레이스 관련 속성 선언)
# REMOTE SHELL
(remote shell 관련 속성)
shell.auth=simple # Authentication type. Auto-detected according to the environment.
shell.auth.jaas.domain=my-domain # JAAS domain.
shell.auth.key.path= # Path to the authentication key. This should point to a valid ".pem" file.
shell.auth.simple.user.name=user # Login user.
shell.auth.simple.user.password= # Login password.
shell.auth.spring.roles=ADMIN # Comma-separated list of required roles to login to the CRaSH console.
shell.command-path-patterns=classpath*:/commands/**,classpath*:/crash/commands/** # Patterns to use to look for commands.
shell.command-refresh-interval=-1 # Scan for changes and update the command if necessary (in seconds).
shell.config-path-patterns=classpath*:/crash/* # Patterns to use to look for configurations.
shell.disabled-commands=jpa*,jdbc*,jndi* # Comma-separated list of commands to disable.
shell.disabled-plugins= # Comma-separated list of plugins to disable. Certain plugins are disabled by default based on the environment.
shell.ssh.auth-timeout = # Number of milliseconds after user will be prompted to login again.
shell.ssh.enabled=true # Enable CRaSH SSH support.
shell.ssh.idle-timeout = # Number of milliseconds after which unused connections are closed.
shell.ssh.key-path= # Path to the SSH server key.
shell.ssh.port=2000 # SSH port.
shell.telnet.enabled=false # Enable CRaSH telnet support. Enabled by default if the TelnetPlugin is available.
shell.telnet.port=5000 # Telnet port.
# GIT INFO
spring.git.properties= # Resource reference to a generated git info properties file.
(git 속성)
# METRICS EXPORT (MetricExportProperties)
(metrics 추출)
spring.metrics.export.aggregate.key-pattern= # Pattern that tells the aggregator what to do with the keys from the source repository.
spring.metrics.export.aggregate.prefix= # Prefix for global repository if active.
spring.metrics.export.delay-millis=5000 # Delay in milliseconds between export ticks. Metrics are exported to external sources on a schedule with this delay.
spring.metrics.export.enabled=true # Flag to enable metric export (assuming a MetricWriter is available).
spring.metrics.export.excludes= # List of patterns for metric names to exclude. Applied after the includes.
spring.metrics.export.includes= # List of patterns for metric names to include.
spring.metrics.export.redis.key=keys.spring.metrics # Key for redis repository export (if active).
spring.metrics.export.redis.prefix=spring.metrics # Prefix for redis repository if active.
spring.metrics.export.send-latest= # Flag to switch off any available optimizations based on not exporting unchanged metric values.
spring.metrics.export.statsd.host= # Host of a statsd server to receive exported metrics.
spring.metrics.export.statsd.port=8125 # Port of a statsd server to receive exported metrics.
spring.metrics.export.statsd.prefix= # Prefix for statsd exported metrics.
spring.metrics.export.triggers.*= # Specific trigger properties per MetricWriter bean name.
# ----------------------------------------
# DEVTOOLS PROPERTIES
# ----------------------------------------
# DEVTOOLS (DevToolsProperties)
(devtools 관련 속성)
spring.devtools.livereload.enabled=true # Enable a livereload.com compatible server.
spring.devtools.livereload.port=35729 # Server port.
spring.devtools.restart.additional-exclude= # Additional patterns that should be excluded from triggering a full restart.
spring.devtools.restart.additional-paths= # Additional paths to watch for changes.
spring.devtools.restart.enabled=true # Enable automatic restart.
spring.devtools.restart.exclude=META-INF/maven/**,META-INF/resources/**,resources/**,static/**,public/**,templates/**,**/*Test.class,**/*Tests.class,git.properties # Patterns that should be excluded from triggering a full restart.
spring.devtools.restart.poll-interval=1000 # Amount of time (in milliseconds) to wait between polling for classpath changes.
spring.devtools.restart.quiet-period=400 # Amount of quiet time (in milliseconds) required without any classpath changes before a restart is triggered.
spring.devtools.restart.trigger-file= # Name of a specific file that when changed will trigger the restart check. If not specified any classpath file change will trigger the restart.
# REMOTE DEVTOOLS (RemoteDevToolsProperties)
(remote devtools 관련 속성)
spring.devtools.remote.context-path=/.~~spring-boot!~ # Context path used to handle the remote connection.
spring.devtools.remote.debug.enabled=true # Enable remote debug support.
spring.devtools.remote.debug.local-port=8000 # Local remote debug server port.
spring.devtools.remote.proxy.host= # The host of the proxy to use to connect to the remote application.
spring.devtools.remote.proxy.port= # The port of the proxy to use to connect to the remote application.
spring.devtools.remote.restart.enabled=true # Enable remote restart.
spring.devtools.remote.secret= # A shared secret required to establish a connection (required to enable remote support).
spring.devtools.remote.secret-header-name=X-AUTH-TOKEN # HTTP header used to transfer the shared secret.